Air Source Heat Pumps
We’re helping homeowners achieve a warm comfortable home/ Achieving this could be easer then you think with high performance, low carbon air source heat pumps.
What is an air source heat pump?
Air source heat pumps are a greener alternative to boiler heating systems. They’re low-maintenance and highly efficient – and they might just cut your heating costs.
Air source heat pumps look a bit like air-conditioning units – and their size depends on how much heat they'll need to generate for your home. The bigger the heat pump, the more heat is produced.
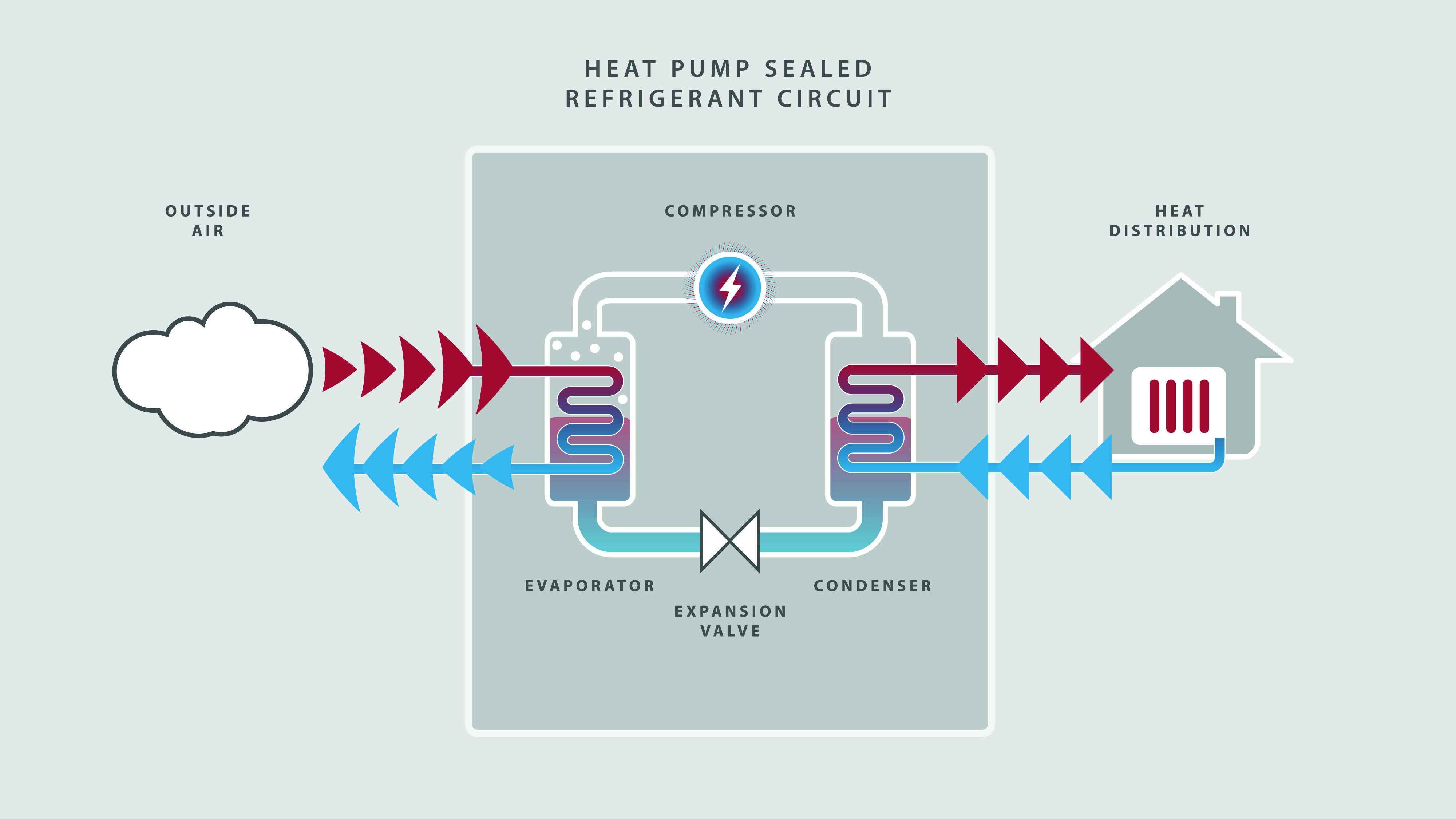
Air source heat pumps use one simple, renewable resource as their main source of energy air. They take energy from the air outside (even when it’s cold) and convert it into heat for your home. They work just like fridges, just in reverse.
The pump absorbs naturally occurring heat from the air and uses this to heat your home and give you hot water. Since it transfers heat, rather than generating it, heat pumps are one of the most efficient means of warming your house.
How do air source heat pumps work?
The heat pump takes in air from outside to heat a liquid refrigerant. The heat turns the liquid into a gas through evaporation.
Electricity runs a pump compressor, compressing the gas, making it even warmer.
This heat is sent to heat your home and hot water cylinder. So, you’ve got a warm home and hot water.
Meanwhile, the liquid refrigerant cools off, getting ready to start the whole process again.
What are the pros and cons of an air source heat pump?
Air source heat pumps are low maintenance, and generally more environmentally friendly than the systems they replace. The main component used to create heat is air a natural, renewable resource. But they’re not suitable for all types of building.
Air source heat pump benefits:
They could lower the costs of heating your home especially if you’re switching from an electric, LPG, oil, or coal-fuelled system.
They produce far fewer carbon emissions than fossil fuel boilers - cutting your carbon footprint as air is a renewable resource. heat pumps don't give off any gases or particulates like gas and oil boilers, which can decrease the quality of the air.
Air source heat pumps work best at lower heating temperatures, so they’re better if you have large radiators, or underfloor heating. Radiators and pipe may need to be replaced
Because they heat to a lower temperature than traditional systems, your will need good insulation and draught proofing, to help keep your home warm.
They only work with homes that have some outside space
They do use some electricity to run. They are not completely carbon neutral. But if you use renewable electricity, the environmental impact is low, and getting lower as more renewables come onto the electricity grid.
The running costs will depend on:
The size of your home – the bigger the space, the more power needed to heat it.
How well insulated your home is - better insulation means less heat loss.
How warm you want your home to be - higher temperatures take more energy.
Whether you have underfloor heating or radiators - typically the larger the “emitter”, the lower the flow temperature, and the more efficiently the heat pump can run.
Air source heat pump savings
Can you really save money with a heat pump? Are they worth it?
Your potential savings will depend on what kind of fuel you’re replacing. If it’s gas, your gas use will go down, but your electricity use will go up. And because air source heat pumps are quite expensive to buy and set up, it could take several years to recoup the costs of installing one.
If, on the other hand, you have an electric, oil, LPG, or coal system – particularly an old, inefficient one – an air source heat pump could work out cheaper.
If you’re building a new home, an air source heat pump could really be the best option. They’re quite simple to install – and you could even include underfloor heating or solar panels to help support the system and make it easier for the pump to heat up your home.
Things to consider before installing an air source heat pump
Air source heat pumps work best with a well-insulated home – so here are some clever ways to boost your home insulation:
- Make sure your loft is well insulated
- Get cavity wall insulation wherever possible
- Get draught excluders for outside doors, windows, and letterboxes
- Replace old windows with double glazing
Other things to think about before you get an air source heat pump:
You’ll need the unit to be installed outside your home, against a wall, with good airflow.
How quickly you could make savings depends on the energy source you already use. If it’s coal or electricity, switching will be more efficient, saving you energy and money.


